线程是一种多任务编程的方式,可以使用计算机多核资源。线程又被称为轻量级的进程
线程特征
* 线程是计算机核心分配的最小单位
* 一个进程可以包含多个线程
* 线程也是一个运行过程,也要消耗计算机资源。多个线程共享其进程的资源和空间
* 线程也拥有自己特有的资源属性,比如指令集,TID等
* 线程无论创建还是删除还是运行资源消耗都小于进程
* 多个线程之间并行执行,互不干扰
from threading import Thread
t = Thread(target, [, args], [kwargs])
创建线程对象
- target 绑定线程函数
- args 元组 给线程函数位置传参
- kwargs 字典 给线程函数键值传参
t.start() 启动线程
t.join([timeout]) 回收线程
import threading
import os
a = 1
# 线程函数
def music():
print("进程pid号", os.getpid())
global a
print("a = ",a)
a = 10000
t = threading.Thread(target=music) # 创建线程对象
t.start() # 启动线程
print("进程pid号", os.getpid())
t.join() # 回收线程
print("Main a:",a)
# 进程pid号 12549
# 进程pid号 12549
# a = 1
# Main a: 10000
os.getpid获取的是进程的pid号,线程是进程中的一个成员.
线程中改的变量,是进程中的变量.并没有新开辟一个空间.
t.is_alive() 查看线程状态
t.name 线程名称 默认Thread-1
t.setName() 设置线程名称
threading.currentThread() 获取当前线程对象
 View Code
View Codet.daemon
默认情况下,主线程的结束不会影响分支线程,如果设置为True则主线程退出分支线程也会退出
设置方法:
t.daemon = True
t.setDaemon()
线程daemon属性的设置在start前;一般设置daemon后不会使用join
- 继承Thread类
- 运行Thread类中的__init__方法以获取父类属性
- 重写run方法
使用方法
- 实例化对象
- 调用start自动化执行run方法
- 调用join回收线程
1.通信方法:线程间使用全局变量进行通信
2. 共享资源争夺
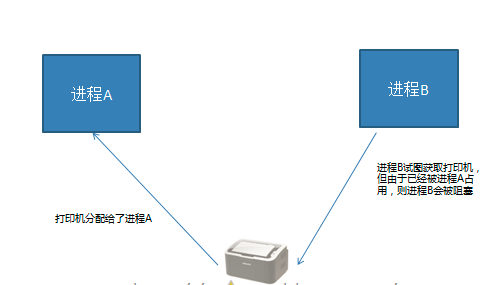
- 共享资源:多个进程或者线程都可以操作的资源称为共享资源。对共享资源的操作代码段称为临界区。
- 影响 :对共享资源的无序操作可能会带来数据的混乱,或者操作错误。此时往往需要同步互斥机制协调操作顺序。
3. 同步互斥机制
同步 : 同步是一种协作关系,为完成操作,多进程或者线程间形成一种协调,按照必要的步骤有序执行操作。
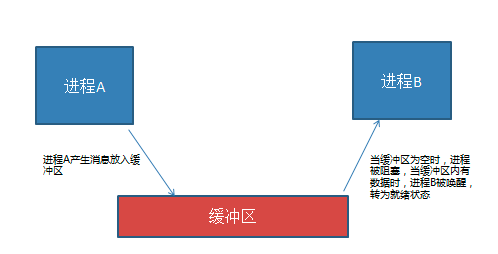
互斥 : 互斥是一种制约关系,当一个进程或者线程占有资源时会进行加锁处理,此时其他进程线程就无法操作该资源,直到解锁后才能操作。
from threading import Event
e = Event() 创建线程event对象
e.wait([timeout]) 阻塞等待e被set
e.set() 设置e,使wait结束阻塞
e.clear() 使e回到未被设置状态
e.is_set() 查看当前e是否被设置
from threading import Lock
lock = Lock() 创建锁对象
lock.acquire() 上锁 如果lock已经上锁再调用会阻塞
lock.release() 解锁
with lock: # 上锁
...
...
with代码块结束自动解锁
python ---》 支持线程操作 ---》IO的同步和互斥 --》 加锁 ----》 超级锁,给解释器加锁
后果:一个解释器,同一时刻只解释一个线程,此时其他线程需要等待。大大降低了python线程的执行效率
* 修改c解释器
* 尽量使用多进程进行并行操作
* python线程可以用在高延迟多阻塞的IO情形
* 不使用cpython c# java做解释器
分别测试 多进程 多线程 单进程执行相同的IO操作和CPU
#计算密集
def count(x,y):
c = 0
while c < 7000000:
x += 1
y += 1
c += 1
#io密集
def write():
f = open("test.txt",'w')
for x in range(2000000):
f.write("hello world\n")
f.close()
def read():
f = open("test.txt")
lines = f.readlines()
f.close()
操作的时间
#单进程程序
from test import *
import time
# t = time.time()
# for i in range(10):
# count(1,1)
# print("Line cpu:",time.time() - t)
t = time.time()
for i in range(10):
write()
read()
print("Line IO:",time.time() - t)
Line cpu: 8.15166711807251
Line IO: 6.841825246810913
from test import *
import threading
import time
counts = []
t = time.time()
for x in range(10):
th = threading.Thread(target = count,args = (1,1))
th.start()
counts.append(th)
for i in counts:
i.join()
print("Thread cpu",time.time() - t)
from test import *
import threading
import time
counts = []
def io():
write()
read()
t = time.time()
for x in range(10):
th = threading.Thread(target = io)
th.start()
counts.append(th)
for i in counts:
i.join()
print("Thread IO",time.time() - t)
Thread cpu 8.414522647857666
Thread IO 6.023292541503906
from test import *
import multiprocessing
import time
counts = []
t = time.time()
for x in range(10):
th = multiprocessing.Process\
(target = count,args = (1,1))
th.start()
counts.append(th)
for i in counts:
i.join()
print("Process cpu",time.time() - t)
from test import *
import multiprocessing
import time
counts = []
def io():
write()
read()
t = time.time()
for x in range(10):
th = multiprocessing.Process(target = io)
th.start()
counts.append(th)
for i in counts:
i.join()
print("Process IO",time.time() - t)
Process cpu 4.079084157943726
Process IO 3.2132551670074463
- 两者都是多任务编程的方式,都能够使用计算机的多核
- 进程的创建删除要比线程消耗更多的计算机资源
- 进程空间独立,数据安全性好,有专门的进程间通信方法
- 线程使用全局变量通信,更加简单,但是需要同步互斥操 作
- 一个进程可以包含多个线程,线程共享进程的空间资源
- 进程线程都独立执行,有自己的特有资源如属性,id, 命令集等
使用情况:
- 一个进程中并发任务比较多,比较简单,适合使用多线程
- 如果数据程序比较复杂,特别是可能多个任务通信比较多 的时候,要考虑到使用线程同步互斥的复杂性
- 多个任务存在明显差异,和功能分离的时候没有必要一定 写入到一个进程中
- 使用python考虑线程GIL问题
- 1. Windows Server 2008 R2永久激活及Chew-WGA v0.9下载(13495)
- 2.Visual Studio 2017中安装visualSVN及使用详解(5330)
- 3.完美解决iis下JWplayer提示Error loading media: File could not be played错误(4152)
- 4.asp.net mvc+jquery easyui开发基础(一)模块首页及增加、修改、删除模块实现(3534)
- 5.Android avax.net.ssl.SSLPeerUnverifiedException: No peer certificate 解决方法(httpClient支持HTTPS的访问方式)(3382)
- 6..Net Mvc中使用Jquery EasyUI控件讲解(一)表格控件datagrid使用介绍(3087)
- 7.asp.net mvc+jquery easyui开发实战教程之网站后台管理系统开发(七)权限管理模块之系统菜单动态生成(3000)
- 8.asp.net mvc+jquery easyui开发实战教程之网站后台管理系统开发(三)登录模块开发(2988)
- 9.asp.net mvc+jquery easyui开发实战教程之网站后台管理系统开发(八)权限管理模块之权限管理实现(2612)
- 10. asp.net mvc+jquery easyui开发实战教程之网站后台管理系统开发(六)权限管理模块之初始数据准备(2573)


